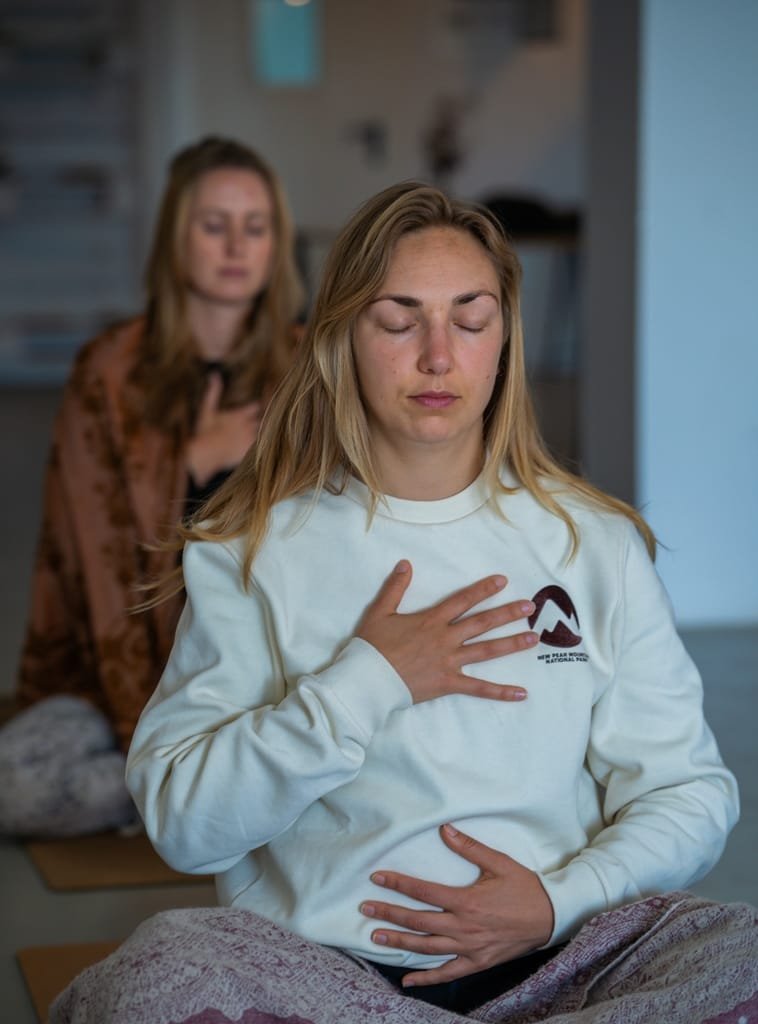

Yoga, a practice that has been around for thousands of years, offers more than just physical fitness; it is a comprehensive approach to health and well-being. Yoga therapy, a subset of this ancient discipline, integrates traditional yogic concepts with modern medical knowledge to treat a variety of ailments and promote overall wellness. This essay delves into the multifaceted benefits of yoga therapy, its philosophical foundations, and its role in contemporary healthcare, illustrating how this holistic practice can transform lives.
The Roots of Yoga Therapy: A Historical Perspective
The origins of yoga can be traced back to ancient India, where it was first mentioned in the sacred texts known as the Vedas, dating back over 5,000 years. The practice evolved through various schools of thought, including the Upanishads, the Bhagavad Gita, and the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali. These texts provided a comprehensive guide to spiritual and physical practices aimed at achieving harmony between the mind, body, and spirit.
Yoga therapy emerged from these roots, combining traditional yogic principles with a therapeutic approach. This integration is evident in texts such as the Hatha Yoga Pradipika and the Gheranda Samhita, which outline various asanas (postures), pranayama (breathing techniques), and dhyana (meditation) designed to promote health and well-being. In modern times, pioneers like Swami Kuvalayananda and T. Krishnamacharya further developed yoga therapy, bridging the gap between ancient wisdom and contemporary science.
The Philosophical Foundations of Yoga Therapy
At the heart of yoga therapy lies the philosophy of holistic health. Unlike conventional medicine, which often focuses on treating symptoms, yoga therapy aims to address the root cause of illness by considering the individual as a whole. This approach is grounded in the principles of Ayurveda, the traditional Indian system of medicine, which emphasizes the balance of the doshas (body energies) and the alignment of the chakras (energy centers).
The holistic nature of yoga therapy is also reflected in the concept of the koshas, or sheaths, which represent the different layers of human existence. According to this model, there are five koshas: the annamaya kosha (physical body), the pranamaya kosha (energy body), the manomaya kosha (mental body), the vijnanamaya kosha (wisdom body), and the anandamaya kosha (bliss body). Yoga therapy seeks to harmonize these layers, promoting health and well-being on all levels.
The Science Behind Yoga Therapy: Bridging Tradition and Modernity
Modern research has provided a wealth of evidence supporting the benefits of yoga therapy. Studies have shown that yoga can improve flexibility, strength, and balance, reduce stress and anxiety, and enhance overall quality of life. Furthermore, yoga therapy has been found to be effective in managing chronic conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, asthma, and arthritis.
One of the key mechanisms behind these benefits is the practice of pranayama, or controlled breathing. Research has demonstrated that pranayama can influence the autonomic nervous system, reducing the stress response and promoting relaxation. This is particularly beneficial for conditions such as anxiety and depression, where dysregulation of the nervous system is often a contributing factor.
Similarly, the practice of asanas, or physical postures, has been shown to positively impact musculoskeletal health. Regular practice of asanas can improve joint mobility, increase muscle strength, and enhance postural alignment. These benefits are particularly relevant for conditions such as osteoarthritis and chronic back pain, where maintaining physical function is crucial.
Yoga Therapy in Practice: Techniques and Applications
Yoga therapy encompasses a wide range of techniques, each tailored to address specific health concerns. These techniques can be broadly categorized into asanas (postures), pranayama (breathing exercises), dhyana (meditation), and shavasana (relaxation). By integrating these practices, yoga therapy offers a comprehensive approach to healing and wellness.
Asanas: Physical Postures for Health and Healing
Asanas form the cornerstone of yoga therapy, offering a wide range of physical benefits. These postures are designed to improve flexibility, strength, and balance, while also promoting relaxation and reducing stress. In yoga therapy, asanas are often adapted to suit the individual’s needs, taking into account factors such as age, fitness level, and specific health conditions.
For example, individuals with chronic back pain may benefit from gentle asanas such as Cat-Cow (Marjaryasana-Bitilasana) and Child’s Pose (Balasana), which help to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the spine. Similarly, individuals with arthritis may find relief through the practice of joint-friendly asanas such as Tree Pose (Vrksasana) and Warrior Pose (Virabhadrasana), which promote joint mobility and stability.
Pranayama: The Breath of Life
Pranayama, or controlled breathing, is a powerful tool in yoga therapy. By regulating the breath, pranayama techniques can influence the autonomic nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing stress. This is particularly beneficial for conditions such as anxiety, depression, and hypertension.
There are various pranayama techniques used in yoga therapy, each with its unique benefits. For example, Nadi Shodhana (Alternate Nostril Breathing) is known for its calming effects, helping to balance the nervous system and reduce stress. Similarly, Bhramari (Bee Breath) is effective in reducing anxiety and promoting a sense of inner peace.
Dhyana: The Art of Meditation
Meditation, or dhyana, is a central component of yoga therapy. By focusing the mind and cultivating a state of inner stillness, meditation can promote mental clarity, reduce stress, and enhance emotional well-being. There are various meditation techniques used in yoga therapy, ranging from mindfulness meditation to guided imagery and mantra meditation.
Mindfulness meditation, for example, involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment. This practice has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, improve concentration, and enhance overall well-being. Guided imagery, on the other hand, involves visualizing positive images and scenarios, helping to promote relaxation and reduce stress.
Shavasana: The Ultimate Relaxation
Shavasana, or Corpse Pose, is often considered the ultimate relaxation pose in yoga therapy. By lying in a supine position and focusing on deep, rhythmic breathing, individuals can achieve a state of deep relaxation and inner peace. This practice is particularly beneficial for reducing stress, improving sleep, and promoting overall well-being.
The Role of Yoga Therapy in Contemporary Healthcare
In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the benefits of yoga therapy in contemporary healthcare. As a holistic approach to health and well-being, yoga therapy offers a complementary and integrative treatment option for a wide range of conditions.
Yoga Therapy for Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is a prevalent issue affecting millions of people worldwide. Conventional treatments often focus on pain relief through medication, which can have side effects and may not address the underlying cause of pain. Yoga therapy offers a holistic approach to managing chronic pain by addressing physical, emotional, and psychological factors.
Research has shown that yoga therapy can be effective in reducing pain and improving function in individuals with chronic pain conditions such as osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, and chronic low back pain. Through the practice of asanas, pranayama, and meditation, individuals can achieve greater physical flexibility, reduce stress, and enhance their overall quality of life.
Yoga Therapy for Mental Health
Mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression are among the leading causes of disability worldwide. Yoga therapy offers a holistic approach to mental health, addressing the mind-body connection and promoting emotional well-being.
Studies have shown that yoga therapy can be effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression, improving mood, and enhancing overall mental health. Through the practice of pranayama, meditation, and relaxation techniques, individuals can achieve a state of inner calm and emotional balance.
Cardiovascular diseases are a leading cause of death globally, and conventional treatments often focus on medication and lifestyle changes. Yoga therapy offers a complementary approach to cardiovascular health by addressing factors such as stress, hypertension, and lifestyle habits.
Research has shown that yoga therapy can be effective in reducing blood pressure, improving cardiovascular function, and promoting overall heart health. Through the practice of pranayama, asanas, and relaxation techniques, individuals can achieve greater cardiovascular health and reduce their risk of heart disease.
Case Studies: Transformative Journeys through Yoga Therapy
The benefits of yoga therapy are best illustrated through the stories of individuals who have experienced its transformative effects. The following case studies highlight the diverse applications of yoga therapy and its profound impact on health and well-being.
Case Study 1: Overcoming Chronic Pain
Mary, a 55-year-old woman, had been suffering from chronic low back pain for over a decade. Conventional treatments, including medication and physical therapy, provided only temporary relief. Frustrated and desperate for a solution, Mary turned to yoga therapy.
Under the guidance of a certified yoga therapist, Mary began a tailored program that included gentle asanas, pranayama, and meditation. Within a few months, she experienced significant improvements in her pain levels and overall function. Through regular practice, Mary was able to reduce her reliance on medication, improve her physical flexibility, and achieve a greater sense of well-being.
Case Study 2: Managing Anxiety and Depression
John, a 40-year-old man, had been struggling with anxiety and depression for several years. Despite trying various treatments, including medication and therapy, he continued to experience symptoms that affected his daily life. Seeking an alternative approach, John decided to explore yoga therapy.
Through a personalized yoga therapy program, John incorporated pranayama, meditation, and relaxation techniques into his daily routine. Over time, he noticed a significant reduction in his anxiety levels and an improvement in his mood. The holistic approach of yoga therapy helped John achieve emotional balance and enhance his overall mental health
Case Study 3: Improving Cardiovascular Health
Linda, a 60-year-old woman, was diagnosed with hypertension and high cholesterol. Despite taking prescribed medications, she struggled to keep her blood pressure and cholesterol levels under control. Seeking a holistic approach, Linda turned to yoga therapy.
With the guidance of a yoga therapist, Linda began a program that included pranayama, gentle asanas, and stress reduction techniques. Over several months, she noticed significant improvements in her blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Her cardiologist was impressed with her progress and reduced her medication dosage. Linda continued her yoga therapy practice, enjoying improved cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
Case Study 4: Enhancing Quality of Life for Cancer Patients
Robert, a 50-year-old man, was undergoing treatment for prostate cancer. The side effects of chemotherapy and radiation left him feeling fatigued, anxious, and depressed. Looking for a complementary therapy to support his recovery, Robert decided to try yoga therapy.
Robert’s yoga therapist designed a gentle program that included restorative asanas, pranayama, and guided meditation. These practices helped Robert manage his stress, reduce his fatigue, and improve his sleep. Over time, he felt more energized and emotionally resilient. Yoga therapy became an integral part of Robert’s cancer treatment, enhancing his quality of life and aiding his recovery.
The Spiritual Dimension of Yoga Therapy: Awakening the Inner Self
While the physical and mental health benefits of yoga therapy are well-documented, its spiritual dimension is equally significant. Yoga, at its core, is a spiritual practice that seeks to awaken the inner self and connect with the divine. This spiritual aspect is deeply embedded in the philosophy and practice of yoga therapy.
The Concept of Self-Realization
In the yogic tradition, self-realization is the ultimate goal. It involves transcending the ego and experiencing a state of union with the divine. This concept is central to yoga therapy, which aims to facilitate self-awareness and spiritual growth.
Through practices such as meditation and pranayama, individuals can quiet the mind and access deeper states of consciousness. This inner journey fosters a sense of peace, purpose, and connection with the divine. For many, yoga therapy becomes a path to self-discovery and spiritual awakening.
The Role of the Chakras
The chakras, or energy centers, play a vital role in the spiritual aspect of yoga therapy. These seven energy centers, located along the spine, correspond to different aspects of physical, emotional, and spiritual health. Balancing the chakras is believed to promote overall well-being and facilitate spiritual growth.
Yoga therapy incorporates various techniques to balance the chakras, including specific asanas, pranayama, and meditation practices. For example, Heart Chakra (Anahata) practices may include heart-opening asanas and loving-kindness meditation, promoting compassion and emotional healing. By working with the chakras, yoga therapy supports the flow of energy and enhances spiritual well-being.
The Practice of Bhakti Yoga
Bhakti yoga, the path of devotion, is another spiritual dimension of yoga therapy. This practice involves cultivating a deep sense of love and devotion to the divine, often expressed through prayer, chanting, and devotional practices.
Incorporating elements of Bhakti yoga into yoga therapy can enhance the spiritual experience and foster a sense of connection with the divine. Practices such as chanting mantras, reciting prayers, and engaging in devotional rituals can be powerful tools for spiritual healing and growth.
Integrating Yoga Therapy into Daily Life: Practical Tips and Guidance
Yoga therapy is a versatile and accessible practice that can be integrated into daily life. Whether you are new to yoga or an experienced practitioner, incorporating yoga therapy into your routine can enhance your overall health and well-being. Here are some practical tips and guidance to help you get started.
Establish a Regular Practice
Consistency is key when it comes to yoga therapy. Establishing a regular practice, even if it’s just a few minutes each day, can yield significant benefits. Find a time that works for you, whether it’s in the morning, during lunch breaks, or before bed, and commit to your practice.
Listen to Your Body
Yoga therapy is a personalized practice that should be tailored to your individual needs and abilities. Listen to your body and avoid pushing yourself beyond your limits. If you have specific health concerns or physical limitations, work with a certified yoga therapist to develop a safe and effective practice.
Incorporate a Variety of Techniques
Yoga therapy encompasses a wide range of techniques, including asanas, pranayama, meditation, and relaxation. Incorporate a variety of practices into your routine to address different aspects of your health and well-being. For example, you might start your day with a few gentle asanas, practice pranayama during your lunch break, and end the day with meditation.
Create a Sacred Space
Creating a dedicated space for your yoga therapy practice can enhance your experience and foster a sense of tranquility. Find a quiet, comfortable space in your home where you can practice without distractions. Consider adding elements such as candles, incense, or calming music to create a peaceful atmosphere.
Practice Mindfulness
Mindfulness is a key component of yoga therapy. Practice being present and fully engaged in each moment, whether you are performing asanas, practicing pranayama, or meditating. Mindfulness can enhance your practice and promote a deeper sense of connection with your inner self.
Seek Guidance from a Certified Yoga Therapist
Working with a certified yoga therapist can provide valuable guidance and support. A yoga therapist can assess your individual needs and develop a personalized practice that addresses your specific health concerns. They can also provide modifications and adjustments to ensure that your practice is safe and effective.
Conclusion: The Transformative Power of Yoga Therapy
Yoga therapy is a holistic and integrative approach to health and well-being that offers a wide range of physical, mental, and spiritual benefits. By combining traditional yogic principles with modern medical knowledge, yoga therapy addresses the root causes of illness and promotes overall wellness.
The practice of yoga therapy encompasses a variety of techniques, including asanas, pranayama, meditation, and relaxation, each tailored to meet the individual’s needs. Through these practices, individuals can achieve greater physical flexibility, reduce stress, enhance mental health, and foster spiritual growth.
The transformative power of yoga therapy is best illustrated through the stories of individuals who have experienced its profound effects. Whether it’s managing chronic pain, reducing anxiety and depression, improving cardiovascular health, or enhancing quality of life for cancer patients, yoga therapy offers a path to healing and well-being.
Ultimately, yoga therapy is not just a practice but a journey of self-discovery and spiritual awakening. By embracing the divine within and connecting with the deeper aspects of our being, we can achieve a state of harmony and inner peace. Through the holistic approach of yoga therapy, we can transform our lives and embrace the divine within.











Leave a comment: