
Cholesterol is produced by the human body naturally. It can also be obtained in some foods in order to be healthy at heart. Cholesterol plays a very crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of the body. Easy Explanation helps you quickly understand how cholesterol affects your heart health.
This cholesterol may, however, turn out to be your greatest enemy too, since excess amounts of the level may cause accumulation of a plaque known as atherosclerosis. It also increases the risk of blood clots that may result in a stroke or a heart attack. Good cholesterol vs bad cholesterol explains why HDL protects your heart while LDL can cause blockages.
How are you supposed to know then whether your cholesterol levels are good or bad? This paper will discuss the difference between bad and good cholesterol, the normal range of cholesterol, and the management of cholesterol. Understanding Good cholesterol vs bad cholesterol helps you make better heart-health decisions.
What Is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a substance that resembles wax and is present in each of the body’s cells. The bulk of cholesterol that your body needs is produced in your liver, with the remainder of it being produced in some foods. Doctors often explain LDL vs HDL to help patients understand good and bad cholesterol. It is spread in the blood wrapped in proteins called lipoproteins, which are of two major profiles: LDL and HDL. HDL vs LDL cholesterol shows the difference between heart-friendly fats and harmful fats in your blood.
Nevertheless, cholesterol is essential for the following:
- Cell membrane building
- Secretion of hormones estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol.
- Vitamin D is synthesized in the skin under the sun.
- Helping the digestive bile production.
Cholesterol is also vital in a healthy brain. The brain is the place where almost a quarter of cholesterol is located in the body, and which helps to streamline the communication between the nerves and the development of synapses. Doctors often explain Good cholesterol vs bad cholesterol to show how each affects artery health.
It is crucial to memory, learning and cognitive functioning, and it is worth noting that cholesterol is not only essential to the heart but also to total optimum neurological functioning. What is cholesterol in simple terms? Cholesterol is a waxy substance your body needs, but it must stay balanced.
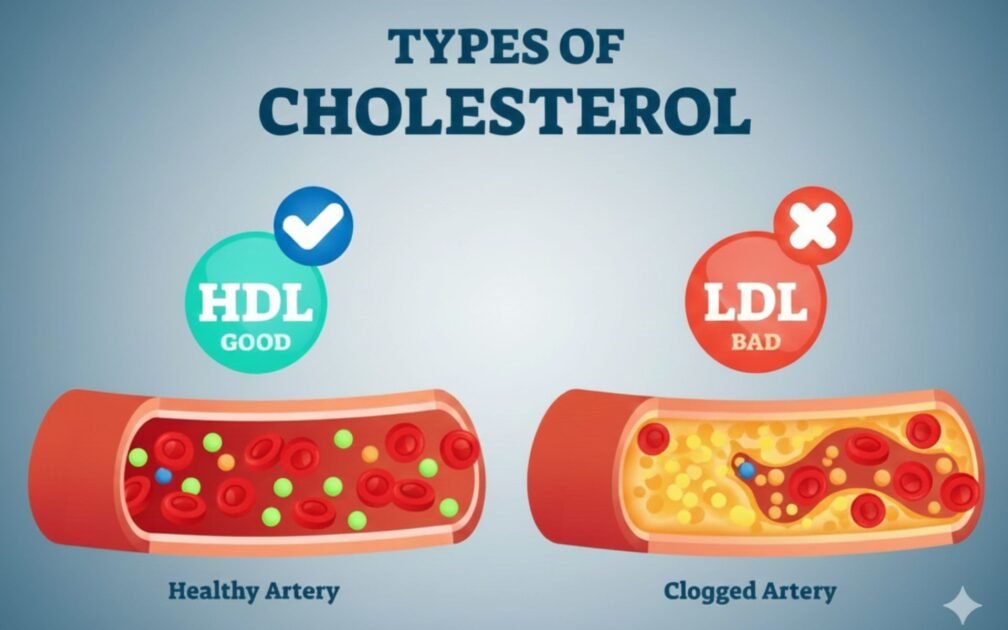
Good Vs. Bad Cholesterol: What to Know?
The lipoproteins are the ones that carry the cholesterol in your blood. They consist of proteins, fats and may be classified into two groups- HDL and LDL. Healthy cholesterol levels help you maintain the right HDL and LDL balance for a strong heart. Knowing LDL vs HDL helps you make better heart-healthy food choices.
LDL – Bad Cholesterol: An Overview
Good cholesterol may become bad cholesterol when the level of cholesterol exceeds the necessary level. The bad cholesterol is the LDL or low-density lipoprotein because it carries the cholesterol to your arteries, where it can be deposited in the vessel walls, resulting in the development of plaque. When comparing Good cholesterol vs bad cholesterol, HDL is seen as protective. It also constricts and thickens your arteries and lines the blood vessels’ walls, obstructing the passage of blood and oxygen to your heart and other body parts.
Failure to control the high LDL cholesterol over an extended period of time may lead to serious health complications such as heart attack, stroke, peripheral disease, or kidney disease. Foods to control cholesterol include oats, nuts, fiber-rich fruits, and healthy fats that support better heart health.
HDL – Good Cholesterol: An Overview
The good cholesterol is HDL, or high-density lipoprotein, since it picks up the cholesterol and transports it to your liver, where it gets broken down and excreted out of your body. Fitness experts talk about LDL vs HDL to highlight the role of exercise in cholesterol control. Thus, HDL will help to prevent the cholesterolfrom building up in your arteries and will make your heart healthier. Many diet plans focus on Good cholesterol vs bad cholesterol improvement for better wellness.
Good Cholesterol (HDL) vs. Bad Cholesterol (LDL)
The “good” and “bad” labels refer to how specific lipoproteins manage cholesterol in your system.
| Feature | HDL (Good Cholesterol) | LDL (Bad Cholesterol) |
| Full Form | High-Density Lipoprotein | Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| Function | Acts like a “vacuum cleaner,” removing excess cholesterol from the arteries and carrying it back to the liver for disposal. | Transports cholesterol to the body’s cells, but excess amounts can stick to artery walls. |
| Effect on Heart | Protects against heart attack and stroke by clearing plaque-forming cholesterol deposits. Higher levels are better. | Damages arteries by contributing to fatty buildups called plaque (atherosclerosis), narrowing the vessels and increasing the risk of blockage. Lower levels are better. |
The Danger of Cholesterol Imbalance
The excess of LDL cholesterol in the blood causes a deposition of plaque in the inner walls of the arteries. Many health reports compare LDL vs HDL to measure overall cardiovascular risk. This deposition makes arteries narrow and rigid and prevents the blood flow to vital organs, which is known as atherosclerosis. When a fragment of plaque bursts, a blood clot may develop and block an artery, resulting in a heart attack or stroke. Learning Good cholesterol vs bad cholesterol can prevent long-term heart risks.
Optimal Cholesterol Ranges
Having known the bad and the good cholesterol, what should be the optimum cholesterol levels? Good cholesterol, i.e., HDL, and bad cholesterol, i.e., LDL, should be in high and low proportions, respectively, to ensure that your body is functioning and your heart is healthy. People often misunderstand Good cholesterol vs bad cholesterol, leading to poor diet choices.
In addition, remember that you cannot diagnose high cholesterol through the symptoms that are observable. Fitness experts highlight Good cholesterol vs bad cholesterol to motivate healthy habits. Cholesterol can only be produced through blood tests, which measure the amount of cholesterol present in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Once you have checked your cholesterol level, your optimal levels should be:
- Total cholesterol: This should be less than 200 mg/ dL.
- Triglycerides: This should be below 150mg/dl.
- HDL: It should be higher than 45mg/dL among males and 55mg/dL among females.
- LDL: In people who do not have any heart disease, diabetes, or blood vessel disease, the LDL level must be less than 130mg/dl. It must not exceed 100mg/dL in those with such medical conditions or high cholesterol.
- VLDL: It is not exceeded by more than 30mg/dL.
How To control the levels of Cholesterol?
Heart-healthy lifestyle consumption of increased soluble fiber (oats, beans, fruits), healthy fats (fish, nuts, olive oil), and plant sterols and less saturated/trans fats (fatty meats, fried foods, baked goods) may be used to lower blood cholesterol. Your doctor may check Good cholesterol vs bad cholesterol during routine blood tests. Add this to regular body workouts, weight loss, smoking cessation, and alcohol reduction, and in case you require it, your doctor can give you some other medications, such as statins, to produce greater effects. Learning about LDL vs HDL is essential for maintaining long-term heart health.
Dietary Changes
- Eat More Soluble Fiber: Oats, beans, lentils, apples, citrus fruits, barley, and psyllium prevent the absorption of cholesterol.
- Consume Healthy Fats: Eat omega-3s (salmon, mackerel) and unsaturated fats (nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil).
- Block absorption: Plant sterols/stanols, which occur in whole grains, nuts, and fortified juices, block absorption.
- Limit Saturated and Trans Fats: limit fats and fatty red meat, full-fat dairy, processed meat (bacon, sausage), fried food, and baked goods.
- Select Lean Proteins: Select skinless chicken, fish, beans, and lentils instead of fatty meats.
Lifestyle Habits
- Be Active: For example, moderate physical activity such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling should be done at least 150 minutes/week to increase HDL or good cholesterol.
- Lose Weight: A small amount of cholesterol, 5-10 percent of body weight, can be reduced by a long distance by losing it.
- Stop Smoking: This is among the most significant changes that you can make.
- Limit Alcohol: Use or abstain from alcohol.
- Control Stress: Cholesterol levels can be influenced by high levels of stress.
Medical Interventions
- Medication: When lifestyle changes fail, physicians use statins (such as atorvastatin, simvastatin) or other medications to reduce LDL cholesterol.
- Professional Guidance: The doctor should help you develop a plan that is unique to you, especially when there is an underlying heart disease.
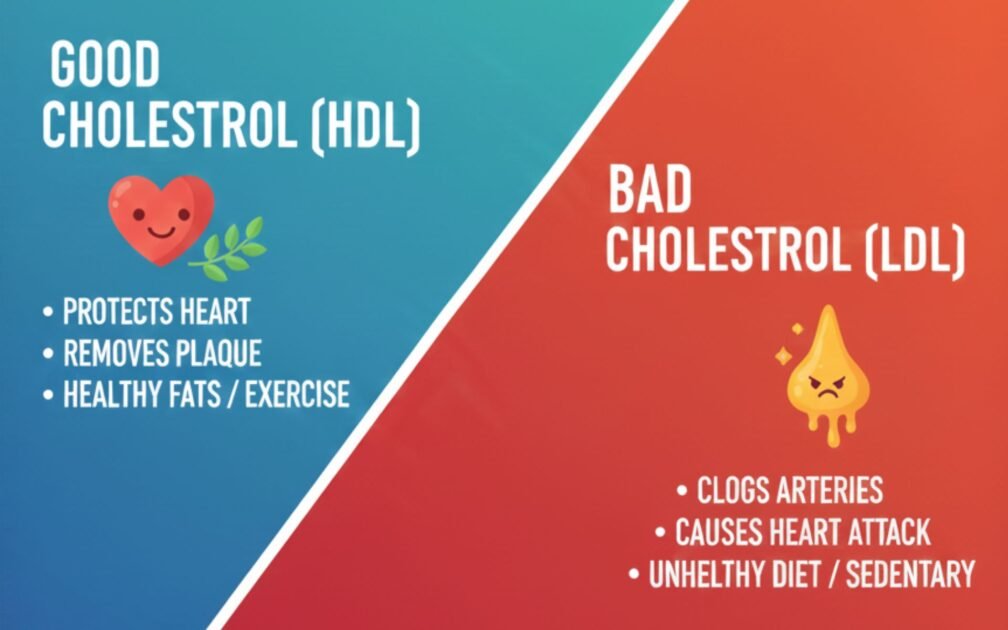
Conclusion
Knowing cholesterol will enable you to keep your heart and your health safe. Not the entire cholesterol is bad- LDL is harmful, but HDL is protective and required by the body. Knowing Good cholesterol vs bad cholesterol helps you avoid foods that raise LDL levels. The correct balance and reduction of cardiovascular diseases will be maintained by a healthy lifestyle of the heart, a check of cholesterol levels, and an informed diet. You can be proactive and ensure that you enjoy the cholesterol and not be too harmful. Your greatest partners in the quest to have optimal heart health are regular exercise and good nutrition, coupled with regular medical check-ups.











Leave a comment: